Understanding Apraxia of Speech: Comprehensive Guide
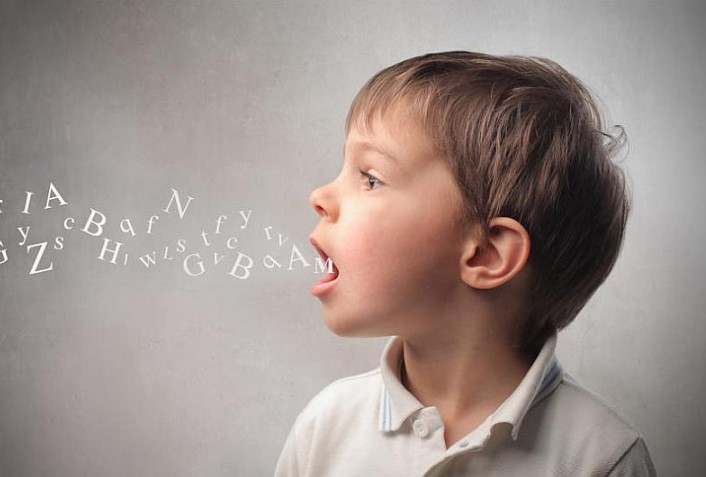

What is Apraxia of Speech?
Apraxia of Speech (AOS) is a neurological condition that affects an individual’s ability to plan and execute the movements necessary for speech. Unlike other speech disorders, AOS is not related to muscle weakness or paralysis. Instead, it involves a disruption in the brain’s ability to send the correct signals to the muscles involved in speaking. This article delves deeply into the intricacies of apraxia of speech, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Symptoms of Apraxia of Speech
Identifying apraxia of speech can be challenging due to its overlap with other speech disorders. However, several hallmark symptoms can help differentiate it:
Inconsistent Speech Errors
Individuals with AOS often exhibit inconsistent speech errors. This means that they may struggle to say a word correctly one time and then mispronounce it the next, even under similar conditions. This inconsistency is a key feature of apraxia.
Difficulty with Speech Initiation
Difficulty initiating speech is another common symptom. Those with AOS might know what they want to say but find it hard to get started. This can lead to frustration and anxiety, further complicating communication efforts.
Groping for Sounds
People with apraxia often engage in groping behaviors, where they physically struggle to find the right sounds and words. This may involve repeated attempts and visible effort to produce speech.
Prosody and Intonation Issues
Prosody refers to the rhythm and flow of speech. Individuals with AOS often have disrupted prosody, resulting in monotone speech or abnormal stress patterns. They might also have difficulty with intonation, making their speech sound robotic or unnatural.
Causes of Apraxia of Speech
The causes of AOS can be divided into two main categories: acquired and developmental.
Acquired Apraxia of Speech
Acquired AOS typically results from damage to the brain due to injury, stroke, or neurodegenerative diseases. This form of apraxia can occur at any age and is often associated with other neurological conditions such as aphasia.
Developmental Apraxia of Speech
Developmental AOS, also known as Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS), is present from birth. The exact cause is often unknown, but it is believed to be related to genetic factors or abnormalities in brain development. Children with CAS have difficulty learning and executing the motor plans necessary for speech from a young age.
Diagnosis of Apraxia of Speech
Accurate diagnosis of AOS is crucial for effective treatment. The process typically involves a comprehensive assessment by a speech-language pathologist (SLP).
Speech and Language Evaluation
An SLP will conduct a thorough speech and language evaluation to assess the individual’s speech production, including articulation, prosody, and the ability to perform non-speech movements. This evaluation helps in identifying the specific characteristics of apraxia.
Neurological Examination
A neurological examination is often necessary to rule out other underlying conditions. This may involve imaging studies like MRI or CT scans to look for brain lesions or abnormalities.
Differential Diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is essential to distinguish AOS from other speech disorders such as dysarthria or aphasia. This involves a detailed analysis of the speech patterns and error types.
Treatment Options for Apraxia of Speech
Effective treatment for AOS requires a personalized approach tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Here are some of the most common and effective treatment strategies:
Speech Therapy
Speech therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for apraxia of speech. The primary goal is to improve the individual’s ability to produce clear and understandable speech. Techniques used in speech therapy may include:
- Repetition and Practice: Repeated practice of speech sounds and words to build motor memory.
- Cueing Techniques: Using visual, auditory, or tactile cues to help the individual produce the correct sounds.
- Pacing Strategies: Teaching the individual to slow down their speech to improve accuracy.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
For individuals with severe AOS, augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) methods may be recommended. These can include:
- Communication Boards: Tools that use pictures or symbols to facilitate communication.
- Speech-Generating Devices: Electronic devices that produce speech when the user selects words or phrases.
Home Practice and Family Involvement
Home practice is vital for reinforcing the skills learned in therapy. Family involvement can greatly enhance the effectiveness of treatment. Educating family members about AOS and involving them in practice sessions can provide crucial support and encouragement.
Pharmacological and Surgical Interventions
In some cases, pharmacological treatments or surgical interventions might be explored, especially if AOS is related to a neurological condition. However, these are less common and typically considered when traditional speech therapy approaches are not sufficient.
Living with Apraxia of Speech
Living with AOS can be challenging, but with the right support and strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for managing daily communication:
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment at home and work can make a significant difference. This includes being patient, encouraging, and providing ample time for the individual to express themselves.
Utilizing Technology
Utilizing technology can enhance communication. Apps designed for speech practice, as well as AAC devices, can be valuable tools.
Joining Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the challenges of living with AOS. These groups can be a source of encouragement and community.
Future Directions in Apraxia Research
Ongoing research is vital to better understand and treat AOS. Current areas of investigation include:
- Genetic Studies: Exploring the genetic basis of developmental AOS to identify potential risk factors.
- Neuroimaging Research: Using advanced imaging techniques to study brain activity and structure in individuals with AOS.
- Innovative Therapies: Developing new therapeutic approaches, including technology-based interventions and motor learning techniques.
Conclusion
Apraxia of Speech is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. With early intervention, personalized therapy, and ongoing support, individuals with AOS can improve their communication abilities and quality of life. For more detailed information and resources on speech disorders and therapy options, consider consulting with a speech-language pathologist or visiting specialized websites.