Amnesia: Understanding Memory Loss and Its Impacts
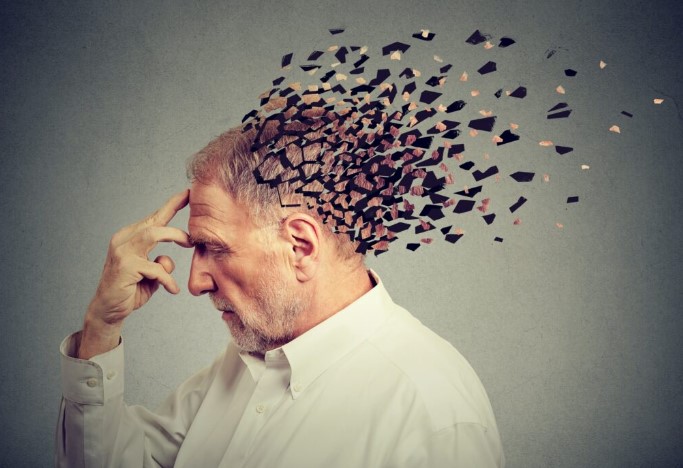


Amnesia is a fascinating yet daunting condition that significantly affects an individual’s ability to remember information. Let’s dive into the world of amnesia to understand what it is, its causes, symptoms, treatments, and how it impacts lives.
Introduction to Amnesia
Amnesia is a condition characterized by a significant loss of memories, such as facts, information, and experiences. Unlike common forgetfulness, amnesia can profoundly disrupt daily life and personal identity.
Types of Amnesia
Understanding the different types of amnesia is crucial to grasping the nuances of this condition:
Retrograde Amnesia
This type involves the loss of pre-existing memories before the onset of amnesia. It’s like having the pages of your life’s book ripped out, making it hard to recall past events.
Anterograde Amnesia
Conversely, anterograde amnesia affects the ability to form new memories after the onset of the condition. Imagine watching a movie but being unable to remember the scenes that just happened.
Transient Global Amnesia
This rare form involves temporary, sudden episodes of memory loss that typically resolve within a few hours. It’s mysterious and often alarming for those who experience it.
Infantile Amnesia
We all experience this to some extent—it’s the inability to recall memories from early childhood, typically before the age of 3-4 years. This phenomenon is a natural part of human development.
Causes of Amnesia
Amnesia can arise from various factors, broadly categorized into neurological, psychological, and medical causes.
Neurological Causes
Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injuries from accidents or physical trauma can damage memory-related brain regions, leading to amnesia.
Stroke
Strokes can disrupt blood flow to the brain, causing memory loss if areas involved in memory processing are affected.
Psychological Causes
Severe Trauma
Psychological trauma, especially from events causing intense stress or fear, can trigger dissociative amnesia, where a person cannot recall personal information.
Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact brain function and memory, sometimes leading to memory lapses.
Medical Causes
Alcohol Abuse
Long-term alcohol abuse can result in Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a severe memory disorder.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications can affect memory, leading to temporary or long-term amnesia as a side effect.
Symptoms of Amnesia
Recognizing the symptoms of amnesia is vital for early intervention:
- Memory Loss: Difficulty recalling past events or forming new memories.
- Confusion: Disorientation regarding time, place, and identity.
- Inability to Recognize Familiar Places or People: Struggling to identify known environments or individuals.
Diagnosing Amnesia
Diagnosing amnesia involves several steps to pinpoint the type and cause:
Medical History Evaluation
A thorough review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms helps in identifying potential causes of amnesia.
Cognitive Tests
Tests assessing memory, problem-solving skills, and other cognitive functions provide insights into the severity and type of amnesia.
Brain Imaging
Techniques like MRI and CT scans reveal structural issues or damage in the brain that may be causing memory problems.
Treatment and Management of Amnesia
While there’s no one-size-fits-all treatment for amnesia, several approaches can help manage the condition:
Medications
Certain drugs can improve symptoms, especially if amnesia is due to a neurological condition.
Therapies
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Therapies aimed at improving cognitive functions and helping patients develop strategies to cope with memory loss.
Psychotherapy
Counseling can assist in dealing with the emotional impact of amnesia and finding effective coping mechanisms.
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in brain-boosting nutrients can support cognitive function.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity enhances overall brain health and can improve memory.
Living with Amnesia
Adapting to life with amnesia involves several coping strategies and support systems:
Coping Strategies
Using tools like journals, reminders, and digital devices to aid memory.
Support Systems
Relying on family, friends, and support groups to navigate daily challenges.
Impact on Daily Life
Amnesia can affect personal relationships, work, and daily activities, making strong support networks essential.
Preventing Amnesia
While not all types of amnesia can be prevented, certain measures can reduce risk:
Brain Health Maintenance
Engaging in activities that stimulate the brain, such as puzzles and learning new skills.
Avoiding Head Injuries
Wearing helmets and taking precautions to prevent head trauma.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Practicing stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises.
Amnesia in Popular Culture
Amnesia is a popular theme in movies and TV shows, often dramatized to add suspense and intrigue. This representation can shape public perception, sometimes leading to misconceptions about the condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial to uncovering more about amnesia and developing better treatments. Advances in neuroscience and cognitive psychology continue to enhance our understanding and approach to this complex condition.
Conclusion
Amnesia is more than just a plot twist in a thriller; it’s a serious condition that affects many people worldwide. By understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and treatments, we can better support those who live with it and advance our knowledge of the human brain.
FAQs
What are the early signs of amnesia? Early signs include frequent memory lapses, confusion about dates or times, and difficulty recognizing familiar people or places.
Can amnesia be reversed? In some cases, particularly those caused by reversible factors like medication side effects, memory can be restored. However, it varies greatly depending on the cause.
How long does amnesia last? The duration of amnesia can range from a few hours (in transient global amnesia) to a lifetime (in severe cases of neurological damage).
Is amnesia common? Amnesia is relatively rare compared to other cognitive impairments but can occur more frequently in certain populations, such as those with brain injuries or severe psychological trauma.
What should you do if someone shows signs of amnesia? Seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare professional can conduct tests to determine the cause and recommend appropriate treatment.