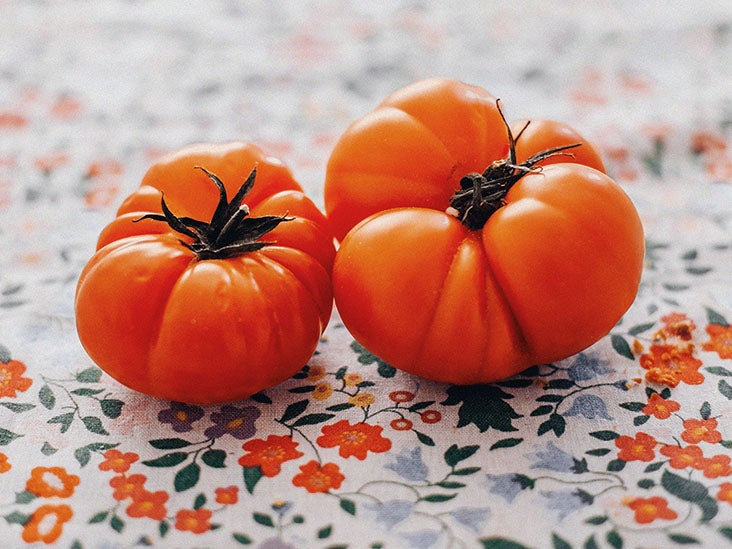
Tomatoes linked to improved gut health, study finds


- A current research noticed the results of tomato usage on the intestine microbiome in pigs.
- Right after 10 piglets were fed a diet of which 10{b574a629d83ad7698d9c0ca2d3a10ad895e8e51aa97c347fc42e9508f0e4325d} was freeze-dried tomato powder, their ratio of “good” to “bad” microbes shifted towards a much more favorable profile.
- The tomato-fed pigs also obtained larger variety in their gut microbial community, believed to be a signifier of stronger intestine wellbeing.
- The results could likely guide to nutritional tips for prolonged-expression wellness in individuals.
Rich in the antioxidant lycopene and other important vitamins and minerals, tomatoes are regarded for their health and fitness added benefits.
But lesser understood are the implications tomato usage has for gut overall health.
In a new examine, researchers examined the outcomes of a tomato-large diet regime on the intestine microbiome employing an animal design.
Scientists fed piglets a tomato-supplemented food plan for 14 times and found that the stability of their gut microorganisms shifted towards a much healthier, a lot more favorable profile.
The final results ended up just lately published in Microbiology Spectrum.
Direct study writer Jessica Cooperstone, Ph.D., assistant professor in the Office of Food stuff Science and Technological know-how at Ohio State University in Columbus, told Health care News Right now:
“Tomato use has been correlated to a range of beneficial health and fitness outcomes, and they are the second most generally consumed vegetable in the United States. About 22{b574a629d83ad7698d9c0ca2d3a10ad895e8e51aa97c347fc42e9508f0e4325d} of overall vegetable ingestion comes from tomatoes, so we are intrigued in far better knowing the health and fitness consequences of this usually eaten meals.”
Researchers made use of 20 male piglets that were being born in the summertime of 2019 at the OSU Swine Facility in Dublin, OH. Just after they have been weaned from their sows, they were being fed a basal eating plan for 1 week.
Up coming, researchers randomly assigned 10 piglets to a tomato food plan consisting of freeze-dried tomato powder extra to the basal diet regime. The remaining 10 piglets received the handle food plan, consisting of the basal diet plan modified to match the tomato diet’s sugar, fiber, and other macronutrient content.
“We wanted to make sure we could give a regular supply of tomatoes to the pigs throughout the review,” Dr. Cooperstone claimed.
“In Ohio, we can only grow tomatoes in the subject for harvest toward the stop of summer time, so freezer drying serves as a preservation stage. We needed to integrate the tomato into the basal diet plan of the pigs, and that diet program is powdered,” she additional.
The tomatoes from which the powder was derived were a hybrid grown at the North Central Agricultural Investigation Station of Ohio Condition College (OSU) in Fremont, OH.
On top of that, to stay clear of any non-nutritional spread of germs, pigs have been housed only with other customers of their group on one particular facet of a walkway. Pens permitted snout-to-snout speak to concerning grouped companions.
At the conclusion of the experiment, there were no entire body-pounds variations concerning the two teams of piglets.
The researchers analyzed fecal samples from all the pigs at the start out of the experiment, 7 days in, and then again soon after 14 days.
Working with DNA
Sequencing detected a shift after 14 days in the ratio of Bacillota (“bad” germs) towards Bacteroidota (“good” microbes).
Both equally varieties or lineages of bacteria, known as phyla, include a big variety of microorganisms, some of which might be beneficial or not.
Scientists also observed a bigger bacterial variety in the samples of the tomato team, which might advise a much healthier
When variety is viewed as helpful in the intestine microbiome, a lot continues to be
Dr. Ashkan Farhadi, a gastroenterologist at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Middle in Fountain Valley, CA, not involved in the review, questioned what could have resulted if the pigs experienced been fed regular tomatoes versus tomato powder.
In addition, whether or not the amount and period of tomato consumption could have yielded unique benefits is not however recognised and might warrant even further analyze.
“There are a whole lot of inquiries that appear out of a good analyze, and this is a superior study,” Dr. Farhadi told MNT.
Dr. Farhadi pointed out that comparisons in between any two species are hard to make definitively.
“We each have intestine germs, [but] are they equivalent involving us? There are no identical germs among even two men and women or in 1 person on two days. Gut germs are so dynamic that even if you are pressured out for a time period of 1 hour, the germs are diverse,” he described.
Though pigs are not people, there is reason to suspect that tomato consumption could possibly equally reward the human microbiome.
“We [are] getting a extra in depth comprehension of how certain foods impression human well being,” Dr. Cooperstone claimed.
“Previous reports have found that the gastrointestinal tract of pigs is far more very similar to humans than mice are to humans, which is why we elected to do this examine in pigs. Other
research have observed that the two main phyla of micro organism in the gut microbiome are the exact same amongst pigs and human beings. We hope to go our trials to human beings in the foreseeable future.”– Jessica Cooperstone, Ph.D., direct author of the analyze
Speaking to Ohio Condition News about the research, Dr. Cooperstone stated that a far better knowledge of the results of distinctive food items on gut wellness “could lead to much more evidence-centered nutritional suggestions for long-expression health.”